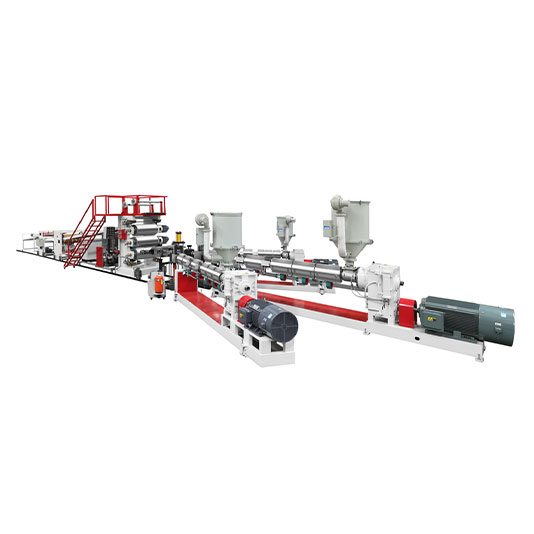
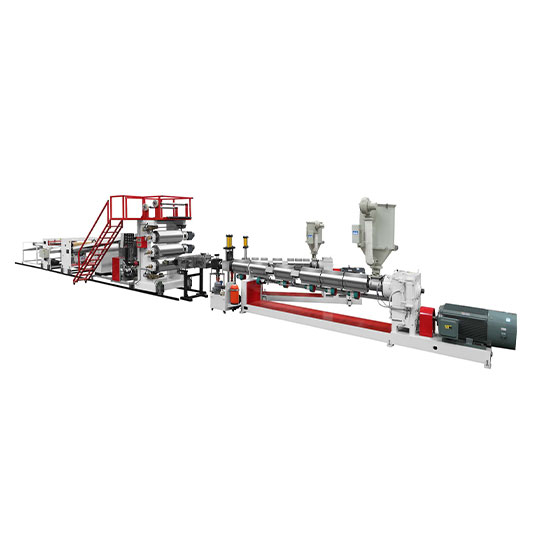
Plastic extrusion machines play a crucial role in the manufacturing of a wide range of plastic products. These machines come in various types, each designed to meet specific production requirements and handle different types of plastics.
1. Single - Screw Extrusion Machines
-
Principle: The single - screw extrusion machine is the most common type. It consists of a hopper, a barrel, and a single - screw conveyor. The screw rotates inside the barrel and transports the plastic material from the hopper to the die. As the screw rotates, it also compresses and melts the plastic through a combination of friction and heat generated by the mechanical action and external heating elements. The molten plastic is then pushed through a die to form the desired shape.
-
Applications: They are widely used for processing a variety of thermoplastic materials such as polyethylene (PE), polypropylene (PP), and polyvinyl chloride (PVC). For example, in the production of simple plastic pipes, plastic sheets for packaging, and plastic profiles for window frames.
-
Advantages: They are relatively simple in design and cost - effective. They are suitable for a wide range of standard plastic extrusion applications and are easy to operate and maintain.
2. Twin - Screw Extrusion Machines
-
Principle: Twin - screw extrusion machines have two intermeshing or non - intermeshing screws inside the barrel. The screws can rotate in the same direction (co - rotating) or in opposite directions (counter - rotating). These machines offer more efficient mixing and conveying of the plastic material. The dual - screw design provides better control over the melting process, heat transfer, and material distribution. The screws can have different geometries to achieve specific mixing and processing requirements.
-
Applications: They are often used for more complex formulations and materials that require a high degree of mixing and homogenization. For example, in the production of filled plastics (plastics with added fillers like glass fibers or carbon nanotubes), masterbatches (concentrated mixtures of additives and polymers), and reactive extrusion processes (where chemical reactions occur during extrusion).
-
Advantages: They provide excellent mixing capabilities, which is crucial for producing high - quality products with consistent properties. They can handle a wider range of materials, including those with poor flow characteristics or those that require precise control over the mixing process.
3. Multilayer Plastic Sheet Extruder Machine
-
Principle: Multilayer Plastic Sheet Extruder Machines are designed to produce products with multiple layers of different plastics. They have multiple extruders, each feeding a different type of plastic material into a single die. The die is specially designed to combine the different layers of molten plastic to form a multi - layered product. The number of layers can vary depending on the application and the design of the machine.
-
Applications: They are used in the packaging industry to produce laminated films and sheets. For example, in the production of food packaging films that have a barrier layer (such as ethylene - vinyl alcohol copolymer, EVOH) sandwiched between layers of other plastics to provide protection against moisture, oxygen, and other gases. Another application is in the production of co - extruded pipes, where different layers of plastics with different properties (such as a corrosion - resistant inner layer and a structurally strong outer layer) are combined.
-
Advantages: They allow for the production of products with enhanced performance characteristics by combining the properties of different plastics. For example, a multi - layer product can have the barrier properties of one plastic and the mechanical strength of another, providing a more versatile and functional end - product.
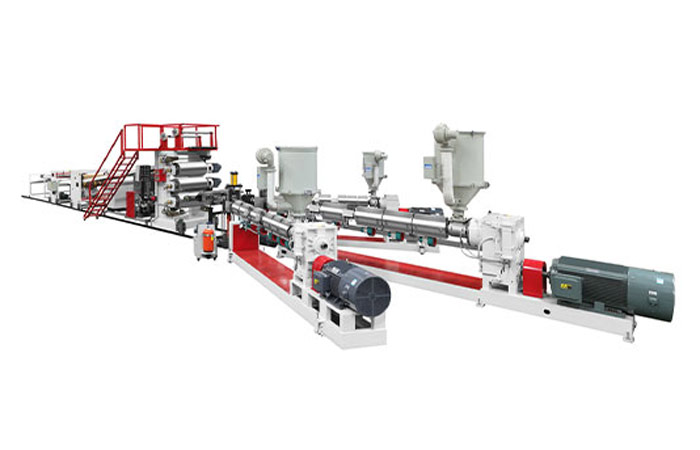

4. Suitcase Sheet Extrusion Machine
-
Principle: Suitcase Sheet Extrusion Machines work on a different principle compared to screw - based extrusion machines. Instead of a continuous screw - driven flow, a ram or a piston is used to push the plastic material through a die. The plastic material is usually pre - formed into a billet or a compacted mass and placed in a chamber. The ram then applies pressure to force the material through the die.
-
Applications: They are used for materials that are difficult to process using screw - extrusion methods, such as highly viscous or filled plastics. For example, in the production of very thick - walled pipes or for extruding plastics with a high proportion of fillers like ceramics or metals.
-
Advantages: They can handle high - viscosity materials effectively and are suitable for producing products with a high degree of compaction. They can also be used for materials that are sensitive to the shear forces generated by screw - extrusion processes.

In conclusion, the different types of plastic extrusion machines offer a wide range of capabilities to meet the diverse needs of the plastic manufacturing industry. Manufacturers can choose the most appropriate machine based on the type of plastic, the complexity of the product, and the production requirements.